We moved our workloads to Kubernetes and now want to run our tests in the cluster. In this series I describe our journey with Testkube. This setup works for us, your milage may vary. You can view all posts in this series by filtering on tag testkube-journey
Where we start
Before Kubernetes we deployed workloads on Windows Virtual Machines. Mostly hosted in Internet Information Services and sometimes as a windows service. The language of choice was (and still is) C# with the Microsoft dotnet runtime.
Our sources are hosted in Azure Devops Server (on-prem). Whenever a new version is committed a build compiles the sources and runs the unittests. The completed build artefact triggers the release pipeline to deploy to the VM. After the deployment the integration tests are run. When all tests are green the installation into production is scheduled for that night.
Full tracking of code to production is in Azure Devops Server.
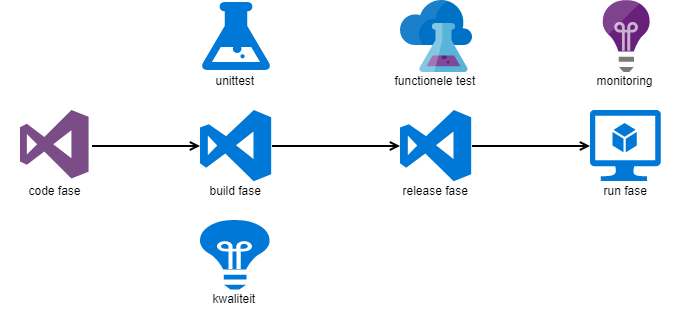
In production we’ve got monitoring. This is added for completeness, but not part of the Testkube journey.
All phases start after the previous completes. Since the complete pipeline is in Azure Devops Server this works great. But with Kubernetes we deploy with gitops and more tools come into play.
Testkube setup
The test orchestration tool of choice is Testkube. It uses Custom Resource Definition (CRD) to store tests. We plan to use gitops for test deployment. Once the tests are in Kubernetes they can be triggered on new versions of the software.
Since we are have no direct internet connection we use the air-gapped installation. This means downloading the chart files from https://github.com/kubeshop/helm-charts/releases and putting them in our local repo. In the values.yaml we needed to specify the global imageRegistry to use our internal image registry and the installation completed without issues.
global:
imageRegistry: "internal-registry-address"
The chart installs:
- mongodb, to store logs
- nats, supporting connectivity component
- minio, to store artifacts (and logs)
- testkube-logs, to collect logs and artifacts
- testkube-api, to interact with Testkube
- testkube-operator, to create kubernetes resources for Testkube
To test the installation we deployed the testkube-cli. The output signals success.
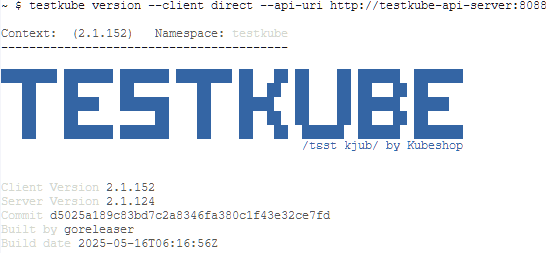
Next step is to create our first TestWorkflow. This will be a future post.